Yves here. Some ahead-of-the-curve analysts have warned of the magnitude of energy debt, mainly junk bonds issued to fund shale gas projects, that are now at risk thanks to plunging oil prices whacking the entire energy complex.
We’ve heard over the last few weeks sunny proclamations of how many shale players have lower cost structure than commonly thought and could ride out weak prices. The supposedly super bearish Bank of America report published earlier in the week called for oil prices to drop to a scary-sounding $50 a barrel. But the document sees that aa a short-term phenomenon. As supply and demand equilibrates (shorthand for “of course some people will drive more, and a lot of wells will get shut down”), it anticipates that oil prices will rebound to $80 to $90 a barrel in the second half of 2015.
The problem with conventional wisdom, even pessimistic-looking conventional wisdom, is that the noose of a lot of borrowings is likely to change the decision-making process of those producers. As the Financial Times’ John Dizard pointed out, companies with a lot of debt are likely to keep pumping, profits be damned, until the money guys choke them off. Banks are already signaling that they will be lenient, but that’s not the same as extending new loans. Nevertheless, the perverse incentive for producers with high debt levels is to keep pumping, even at a loss, in order to generate enough cash flow to keep servicing the debt. That means that wells won’t be shut off as soon as a P&L calculus would indicate, which in turn means the energy oversupply is likely to continue longer than many experts anticipate. Whether that is a mere couple of months or a more dislocating six months plus remains to be seen.
The reason that longer is worse is twofold. First, it means that more players that are seeing if they can hold in the face losses until prices rebound will hit the wall, so that in turn means more banks and junk bond investors will suffer. Second, a longer period of oversupply may lengthen the eventual adjustment period. Bank of America now sees it at six months. If we have an additional six months of not-factored-in overproduction, it could mean even higher inventories before the readjustment begins. That in turn means even lower prices before the turnaround.
And this chart (hat tip Ed Harrison) gives an idea how much a difference the drop from $70 a barrel to yesterday’s below $60 price means (click to enlarge):
And notice that the “half cycle return” is a dubious metric and greatly understates the requirements for meeting long-term profit targets.
By Raúl Ilargi Meijer, editor-in-chief of The Automatic Earth. Originally published at Automatic Earth
Oil producer Russia hikes rates to 10.5% as the ruble continues to plunge, while fellow producer Norway does the opposite, and cuts its rates, but also sees its currency plummet. As Greek stocks lose another 7.35% after Tuesday’s 13% loss on rumors about what the left leaning Syriza party will or will not do if it wins upcoming elections, and virtually anonymous Dubai drops 7.42%. We all know the story of the chain and its weakest link, and beware, these really still ARE global markets.
Meanwhile someone somewhere saved WTO oil from falling through the big, BIG, $60 limit for most of the day Thursday, and then it went south anyway. And that brings to mind the warnings about what would, make that will, happen to high yield energy junk bonds. Of which there’s a lot out there, but not much is being added anymore, that market has been largely shut to companies, especially in the shale patch. So how are they going to finance their fracking wagers? Hard to see.
And something tells me this Bloomberg piece is still lowballing the debt issue, though I commend them for making the link between shale and Fed ‘stimulus’ policies, something all too rare in what passes for press in the US these days.
Fed Bubble Bursts in $550 Billion of Energy Debt
The danger of stimulus-induced bubbles is starting to play out in the market for energy-company debt. Since early 2010, energy producers have raised $550 billion of new bonds and loans as the Federal Reserve held borrowing costs near zero, according to Deutsche Bank. With oil prices plunging, investors are questioning the ability of some issuers to meet their debt obligations. Research firm CreditSights predicts the default rate for energy junk bonds will double to 8% next year. “Anything that becomes a mania – it ends badly,” said Tim Gramatovich, chief investment officer of Peritus Asset Management. “And this is a mania.”
I think it’s obvious that the default rate could be much higher than 8%.
The Fed’s decision to keep benchmark interest rates at record lows for six years has encouraged investors to funnel cash into speculative-grade securities to generate returns, raising concern that risks were being overlooked. A report from Moody’s this week found that investor protections in corporate debt are at an all-time low, while average yields on junk bonds were recently lower than what investment-grade companies were paying before the credit crisis. Borrowing costs for energy companies have skyrocketed in the past six months as West Texas Intermediate crude, the U.S. benchmark, has dropped 44% to $60.46 a barrel since reaching this year’s peak of $107.26 in June.
Yields on junk-rated energy bonds climbed to a more-than-five-year high of 9.5% this week from 5.7% in June, according to Bank of America Merrill Lynch index data. At least three energy-related borrowers, including C&J Energy Services, postponed financings this month as sentiment soured. “It’s been super cheap” for energy companies to obtain financing over the past five years, said Brian Gibbons, a senior analyst for oil and gas at CreditSights in New York. Now, companies with ratings of B or below are “virtually shut out of the market” and will have to “rely on a combination of asset sales” and their credit lines, he said.
When you’re as addicted to debt as the shale industry has been – and still would be if they could still get their fix -, then seeing prices for your products drop over 40% and the yields on your bonds just about double (just for starters), then you have not a problem, but a disaster. And one that’s going to reverberate through all asset markets. It’s already by no means just oil that’s plunging, – industrial – commodities (iron ore, nickel, copper etc.) as a whole are way down from just a few months ago. I read a nice expression somewhere: “the economy is topped with a copper roof”, which supposedly means to say that where copper goes, the economy will follow.
But this is by no means all of the news, it’s not even the worst. To get back to oil, there are some very revealing numbers in the following from CNBC, which call out to us that we haven’t seen nothing yet.
Oil Pressure Could Sock It To Stocks
With crude sliding through the key $60 level, oil pressure could stay on stocks Friday. West Texas Intermediate futures for January closed at $59.95 per barrel, the first sub-$60 settle since July 2009. The $60 level, however, opens the door to the much bigger, $50-per-barrel level. Besides oil, traders will be watching the producer price index Friday morning, and it’s expected to be off 0.1% with the fall in energy. Consumer sentiment is also expected at 10 a.m. EST.
Consumers stepped up and spent in November, as evidenced in the 0.7% gain in that month’s retail sales Thursday. That better mood should show up in consumer sentiment. Stocks on Thursday gave up sizeable gains after oil reversed course and fell through $60.
“Oil has pretty much spooked people,” said Daniel Greenhaus, chief global strategist at BTIG. “There just isn’t a bid. With everything in energy and the oil price collapsing as it is, who is going to step in and be a buyer now? The answer is nobody.” Oil continued to slide in after-hours trading. “The selling appears to have accelerated a little bit after the close with really no bullish news in sight,” said Andrew Lipow, president of Lipow Associates. WTI futures temporarily fell below $59 in late trading.
“The big level is going to be $50 now in terms of psychological support. Much as $100 is on the upside,” said John Kilduff of Again Capital. Oil stands a good chance of getting there too. Tom Kloza, founder and analyst at Oil Price Information Service, said the market could bottom for the winter in about 30 days, but then it will be up to whatever OPEC does.
That was just the intro. Now, wait for it, check this out:
“It’s (oil) actually much weaker than the futures markets indicate. This is true for crude oil, and it’s true for gasoline. There’s a little bit of a desperation in the crude market,” said Kloza.”The Canadian crude, if you go into the oil sands, is in the $30s, and you talk about Western Canadian Select heavy crude upgrade that comes out of Canada, it’s at $41/$42 a barrel.”
“Bakken is probably about $54.” Kloza said there’s some talk that Venezuelan heavy crude is seeing prices $20 to $22 less than Brent, the international benchmark. Brent futures were at $63.20 per barrel late Thursday.
“In the actual physical market, it’s fallen by even more than the futures market. That’s a telling sign, and it’s telling me that this isn’t over yet. This isn’t the bottoming process. The physical market turns before the futures,” he said.
I see very little reason to doubt that what’s happening is that the media are way behind the curve in their reporting of what’s really going on. WTI and Brent are standards, and standards are one thing, but what oil actually sells for is quite another matter. Many companies – and many oil-producing countries too – must sell at whatever price they can get just to survive. And there is no stronger force in the world to drive prices down.
That is today’s reality. And while there are many different estimates around about breakeven prices for US shale plays, if we go with the ones from WoodMacKenzie, we get at least some idea of how bad the industry is hurting with prices below $60 (click to enlarge):
If prices fall any further (and what’s going to stop them?), it would seem that most of the entire shale edifice must of necessity crumble to the ground. And that will cause an absolute earthquake in the financial world, because someone supplied the loans the whole thing leans on. An enormous amount of investors have been chasing high yield, including many institutional investors, and they’re about to get burned something bad.
What it amounts to is that the falling oil price will chase a lot of zombie money out of the markets, the stuff created through a combination of QE-related ultra low interest rates and money printing, plus the demise of accounting standards that allowed companies to abandon mark-to-market practices. This has led to the record stock market valuation that we see today, and that could vanish in the wink of an eye once even just one asset, one commodity, starts being marked to market in defiance of the distortion official policies have imposed upon the global marketplace.
We might well be looking at the development of a story much bigger than just oil. I said earlier this week that it would be hard to find a way to bail out the US oil industry, but that’s merely one aspect here. Because if oil keeps going the way it has lately, the Fed may instead have to think about bailing out the big Wall Street banks once again.
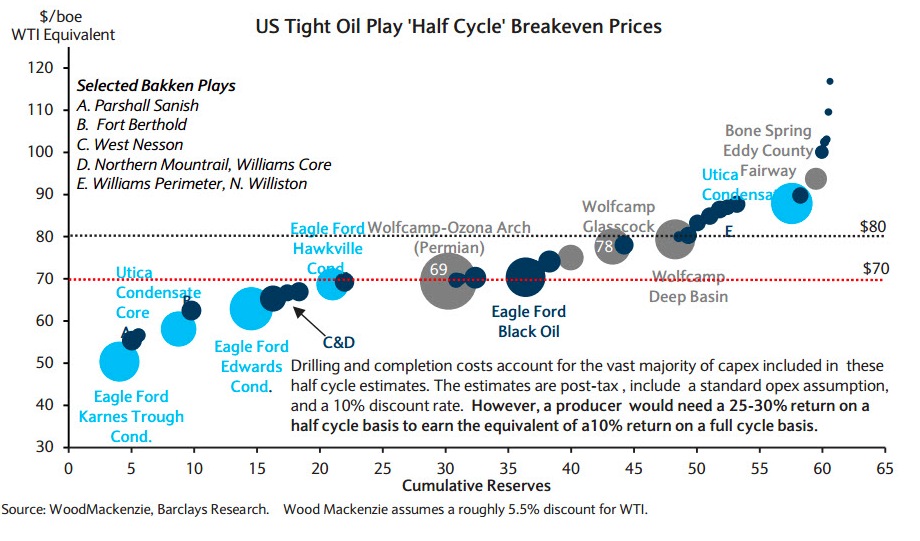
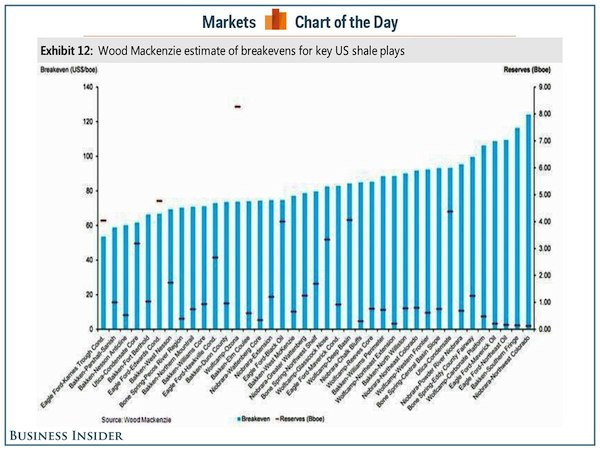


the charts showing the “half cycle” breakeven costs for producing oil in various fields account just for the cost of extraction, & not including other costs such as interest, corporate overhead and the like, nor any environmental remediation….in the lower footnote, the Barclays researchers note that producers would need a 25% to 30% return at those prices to earn 10% on a given project if full cycle accounting were applied…
the widely quoted WTI price is the price for oil delivered to or sitting at the oil storage depot in Cushing OK; prices at the wellhead are sometimes a lot lower, depending on the type of crude oil and the shipping costs to the nearest refinery that can process that type of crude…
I thnk it has become a meme to say that the Fed has pushed investors into high-risk investments through quantitative easing. I have a different opinion. In this post bubbles are depicted as “stimulus-induced” but there is another explanation: bubbles migth well be “inequality-induced”. Higher inequality results in higher savings that are not matched by sane investment opportunities because the demand side is still muted. Those excess savings are invested in less sane investment opportunities generating bubbles. If the Fed raised interest rates it wouldn’t necessarily be the end of bubbles.
“This has led to the record stock market valuation that we see today, and that could vanish in the wink of an eye once even just one asset, one commodity, starts being marked to market in defiance of the distortion official policies have imposed upon the global marketplace”
Ellen Brown also talks about this in her Public Bank Solution book. “The money is simply not there to cover all the liabilities carried on bank balance sheets”. This would include the leveraged loan problem mentioned above as well as interest rate swaps currently trying to be made a liability of depositary institutions.
As Ilargi above she also relates back to our not handling this crisis effectively from the start “An insolvent banking system, in turn, means there can be no “free market.” The market must be controlled.” So we have bailouts and central banks buying equities.
These quotes come from her chapter ‘Quantitative Easing for the People’. It’s becoming very clear that central banks are interested in the health of financial institutions. What we need is an Economic Bill of Rights that covers basic human needs, as Franklin Roosevelt urged in 1944. (This would also increase demand leading to more sane investment opportunities as mentioned by Ignacio above). And a safe place to deposit our savings such as a postal bank that doesn’t engage in speculative activity or lucrative compensation for executives.
I agree with Ignacio and Financial Matters.
The notion that we have ‘free markets’ is risible. We have rigged and manipulated markets as the Central Planners at the Fed try to keep the wheels from completely coming off the oligarchical jalopy. (Is it a rusted-out Bentley?)
So, with the ‘Cromnibus’ legislation, did Congress just now draft us taxpayers to be the fund source to bailout shale bonds? just in time for them, eh?
The problem with conventional wisdom, even pessimistic-looking conventional wisdom, is that the noose of a lot of borrowings is likely to change the decision-making process of those producers. As the Financial Times’ John Dizard pointed out, companies with a lot of debt are likely to keep pumping, profits be damned, until the money guys choke them off.
As more oil is pumped to generate the cash to pay the interest on their debt, even at a loss, the price of oil will decline further which means even more pumping at continuously greater losses.
If prices fall any further (and what’s going to stop them?), it would seem that most of the entire shale edifice must of necessity crumble to the ground.
Yes. Underneath the ground however are thousands of holes with billions of gallons of fracking fluids ready to contaminate water supplies over the next decades. That is on no drillers expense statement. The happy talk commercials by the oil industry and the “STEEL PIPES” put in the ground are nonsense. Consider the earth below the ground surface crumbled where fracking takes place.
No one is looking at gasoline in the $2.00 to $3.00 per gallon range as an opportunity to get a gas guzzler and to go on driving sprees, so just because fuel is a bit less expensive than a year ago doesn’t mean that consumption will increase and raise demand to the point where the drillers can stop sprinting on their debt treadmill. When the “money guys” choke them off, it will be recognition time.
I wonder… as cash gets tighter, how much skimping on fracking contamination mitigation measures will occur? Worst still, what about after abrupt chapter 11 (or worse chapter 7) bankruptcy filings? The expertise to prevent accidental disaster will see their payrolls collapse too. Scary thought.
Of course energy related junk bonds are taking a big hit. The question is the impact on the larger bond market. In a rational world , the negative impact of 15% of the market ( energy ) would be overbalanced by the positive impact this has on the rest of the bond market – lower energy prices should lower default rates due to increased consumer spending. While this is assuredly true over a long enough time frame, rates are not forcasting good times ahead.
I’m still not convinced that this isn’t a good thing for the American economy (the real one; Wall street with its $500bil in junk bonds can go hang; it would be a double bonus if the govt allows it to do so). Despite the shale boom, we are still a net oil importer (albeit less than before). This means that on balance, our country is paying less for energy. If shale production is no longer economic, that just means the money being invested in them is instead available to invest in the rest of the economy.
Why is it considered a good thing when we shut down a U.S. factory and buy the same stuff from a Chinese factory at lower cost, but when the same happens with oil, Wall St. runs around like the sky is falling?
The current situation makes it clear that it was high oil prices, not advances in technology (as we’ve heard endlessly repeated), that brought about the shale boom.
The technology is still there, ladies and gentlemen. Without high prices for oil, however, it cannot be employed.
And the first Aussie company has fallen: http://www.abc.net.au/news/2014-12-11/oil-price-drop-claims-first-wa-victim-red-fork-energy/5962020
Now before you say – but that is Aussie-land – it was funded by US and they drilled in OK. Now back to regular nonsense programming by Fox.
The CEO of Cheniere Energy was on CNBC and had some words of wisdom regarding HY energy debt. The real problems will start a year from now when the hedges come off and the price is still low. After that, debt bombs will go off and the assets will be sold to the next in line. Now instead of $50 break even, it will $20 break even. Pumping will hardly miss a beat. Like I said before, these things will flip like Condo projects gone bust. Someone at the end will make money for a awhile even as demand continues to slide.
Footnote: The CEO of Exxon said last week they plan on adding one and a half million barrels to their total output next year. More blind optimism with the market share spin? I’m sure he’s licking his chops thinking about all those over-leveraged drillers he will swoop down and pick off next year with his stack of cash.
fwiw, the Baker Hughes rig count dropped 29 to 1546 – the biggest weekly drop in 2 years
Just as an observation, I noticed that this week listening to sports talk stations on satellite radio there is a new player in the commercials that sponsor these programs. After having a steady rotation of low testosterone cures and clinics, turn key gym or ‘sports’ hair salons – the new player is an offer to buy your own oil well for those who have a million to invest…